With more than 1,000 bug fixes, Apache Cassandra 4.0 has hit General Availability. It is the most stable release in the project’s history and sets a new high benchmark for distributed databases, having undergone intensive testing to ensure that upgrading and deployments are easy and smooth.
Apache Cassandra 4.0 effortlessly handles unstructured data, with thousands of writes per second. It is community-hardened and tested by Amazon, Apple, DataStax, Instaclustr, iland, Netflix, and others that routinely run clusters as large as 1,000 nodes and with hundreds of real-world use cases and schemas.
"A long time coming, Cassandra 4.0 is the most thoroughly tested Cassandra yet," said Nate McCall, Apache Cassandra committer and PMC chair. "The latest version is faster, more scalable, and bolstered with enterprise security features, ready-for-production with unprecedented scale in the Cloud."
Testing included purpose-built new tools to cover every requirement:
-
Property-based / fuzz testing
-
Replay testing
-
Upgrade / diff testing
-
Performance testing
-
Fault injection
-
Unit / dtest coverage expansion
Those tools were perfected and deployed to help meet quality goals and set a baseline for any future version of Cassandra. They provide needed infrastructure to ensure future releases retain the highest levels of quality and correctness.
So, what can you expect from Cassandra 4.0?
-
Increased speed and scalability – uses Zero Copy Streaming to stream data up to five times faster during scaling operations without virtual nodes (vnodes) and up to 25% faster throughput on reads and writes — which delivers a more elastic architecture particularly in Cloud and Kubernetes deployments.
-
Improved consistency – the fundamentals of the algorithm for incremental anti-entropy repair have been rewritten, which keeps data replicas in sync to optimize incremental repair for faster, more efficient operation and consistency across data replicas. A full repair no longer requires a costly anti-compaction during the preparation phase.
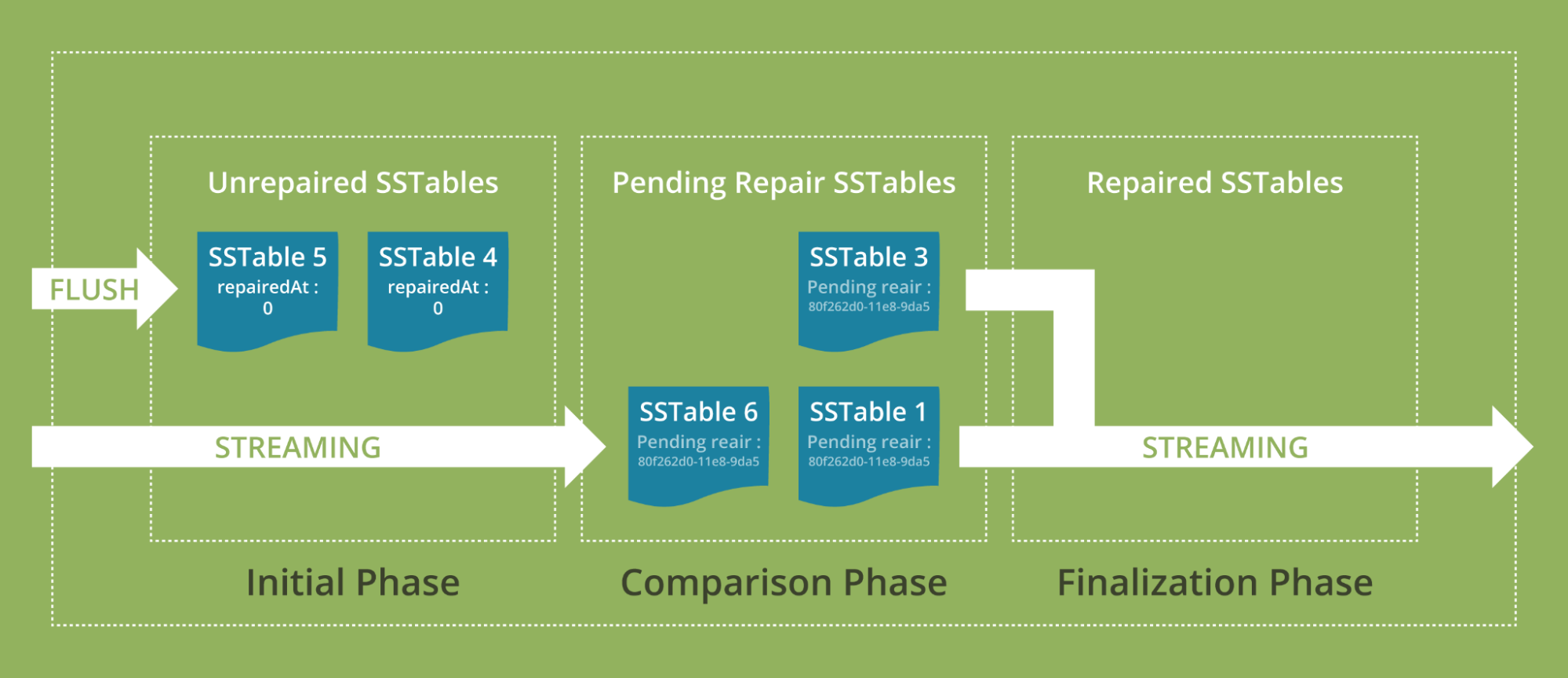
-
New configuration settings – exposed system metrics and configuration settings provide flexibility for operators to ensure they have easy access to data that optimize deployments. Virtual Tables lets you selectively expose system metrics and configuration settings through the Cassandra Query Language (CQL) rather than JMX.
-
Minimized latency – garbage collector pause times are reduced to a few milliseconds with no latency degradation as heap sizes increase. With Java 11 support, version 4.0 uses the garbage collection algorithm ZGC to help teams optimize processes.
-
Enhanced security and observability – audit logging tracks users’ access and activity with minimal impact on workload performance. New capture and replay enables analysis of production workloads to help ensure regulatory and security compliance with SOX, PCI, GDPR, or other requirements. This includes being able to track DML, DDL, and DCL activity with minimal performance hits. There’s also a new FQL tool to capture and replay live traffic data from production for analysis.
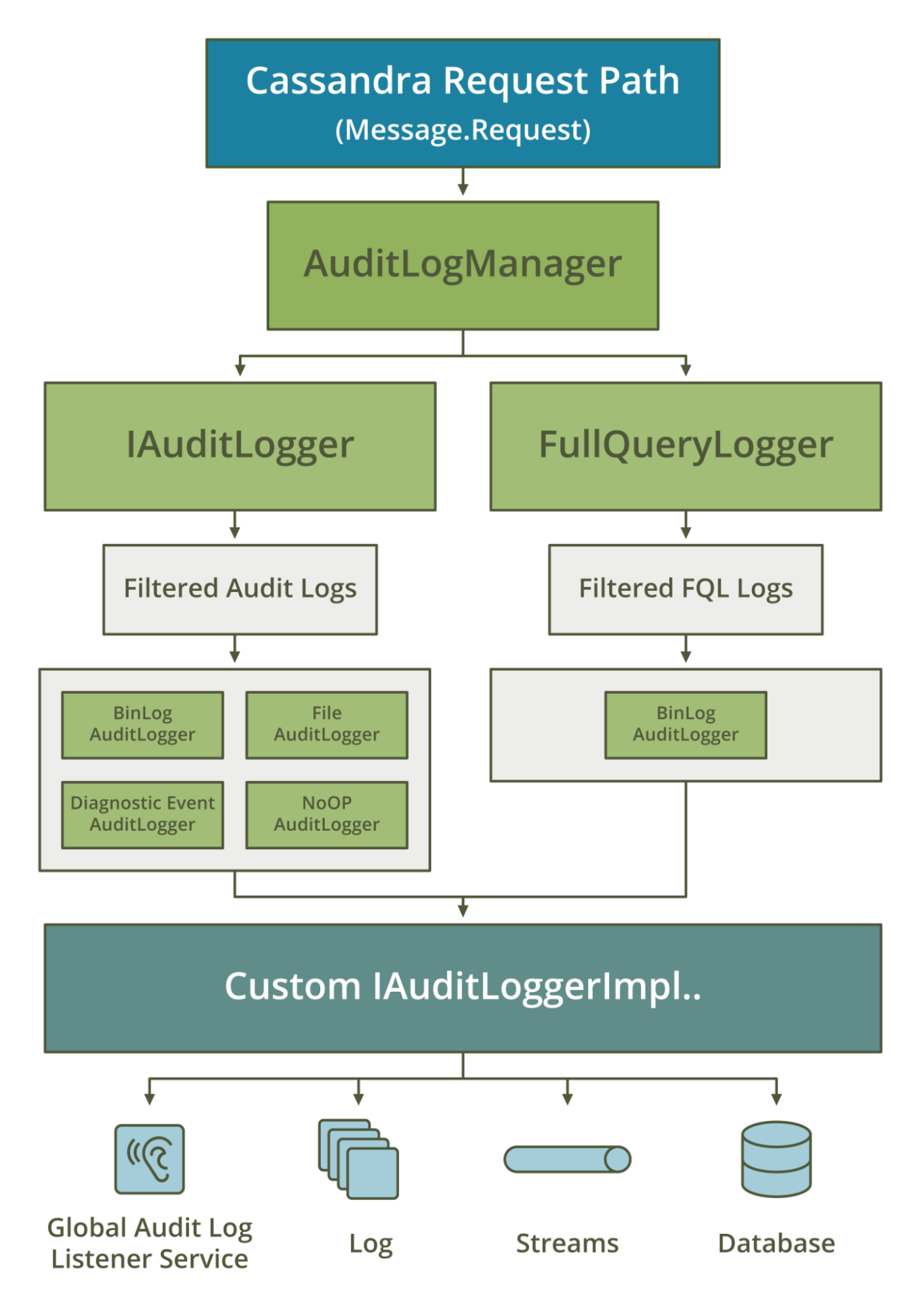
-
Better compression – improved compression efficiency eases unnecessary strain on disk space and improves read performance. Compression is configured on a per-table basis and v4.0 supports Zstandard (Zstd), the data compression algorithm.
-
A shift to a 12-month release cycle, with releases to be supported for a three-year term.
Let the community know via the Apache Cassandra mailing list or Slack if you do run into any bugs.
You can download Apache Cassandra, documentation, and ways to become involved with the Apache Cassandra community by visiting /[cassandra.apache.org/] and https://twitter.com/cassandra.














